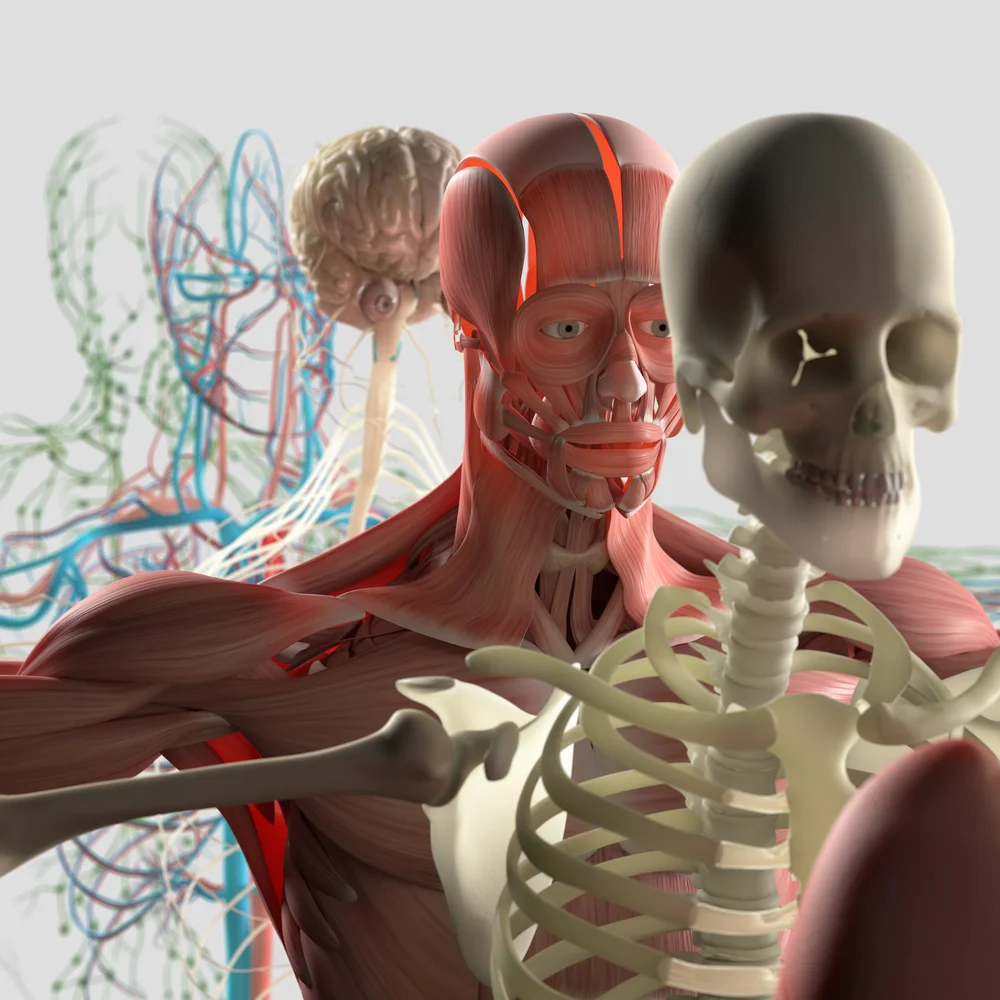
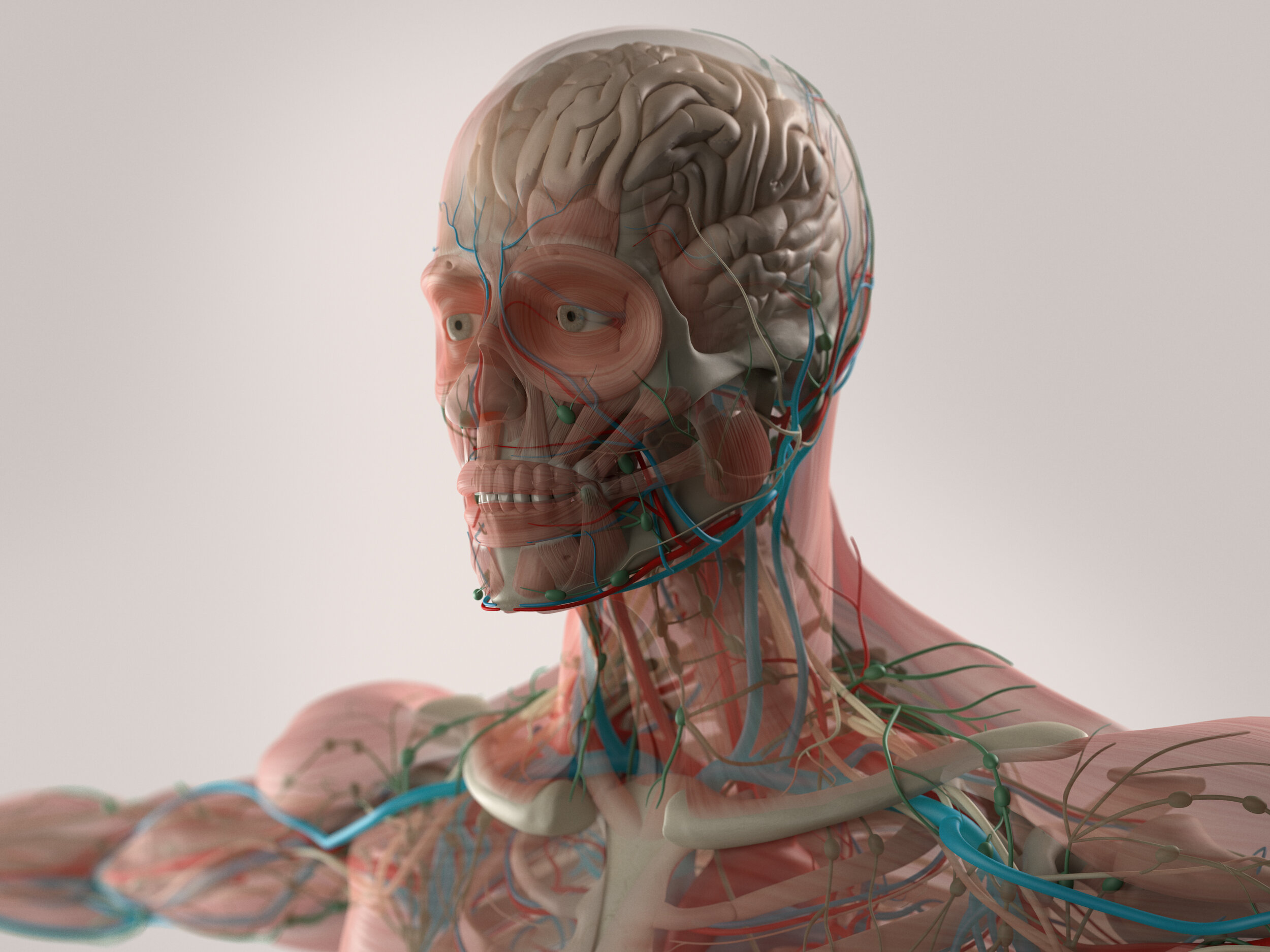
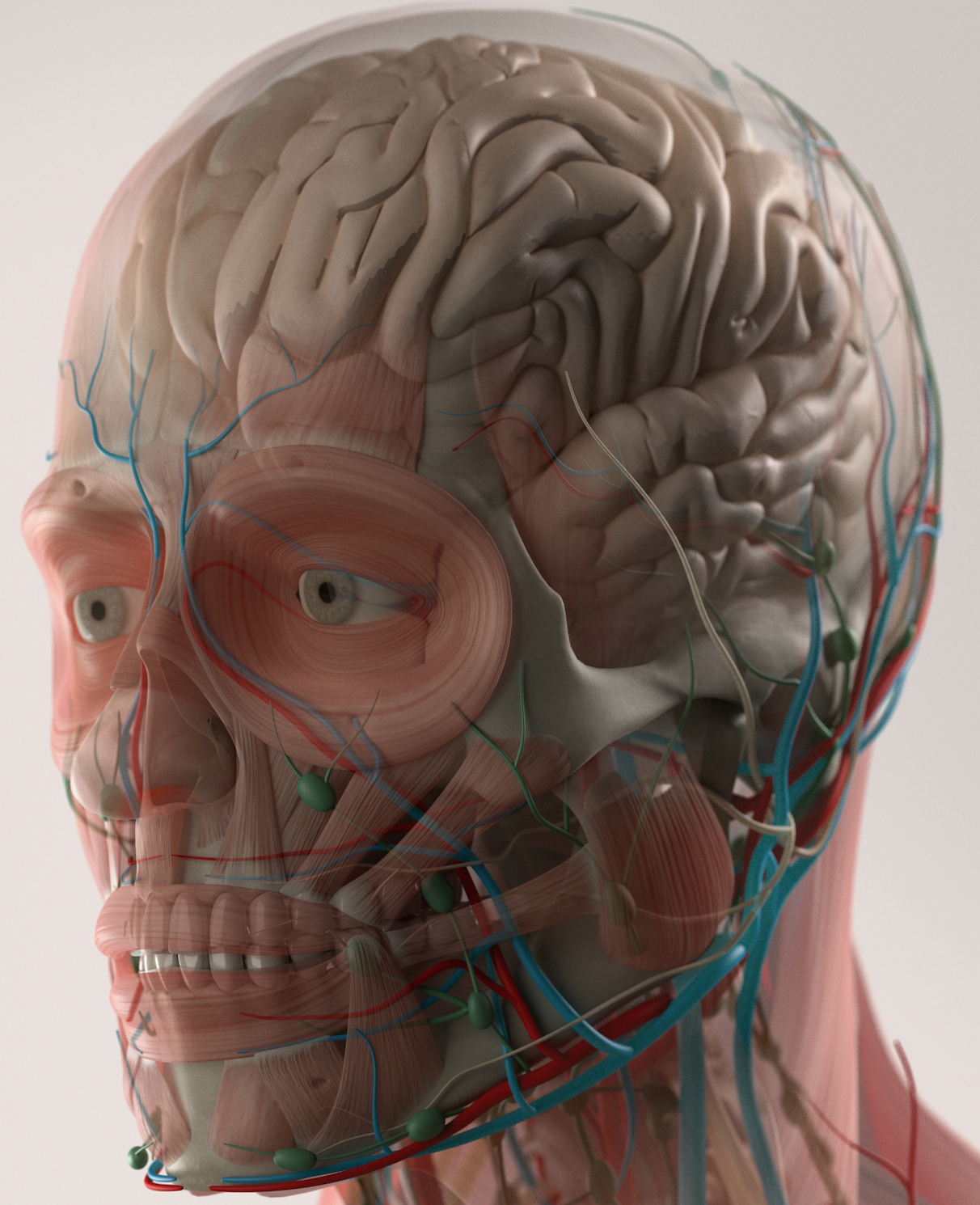
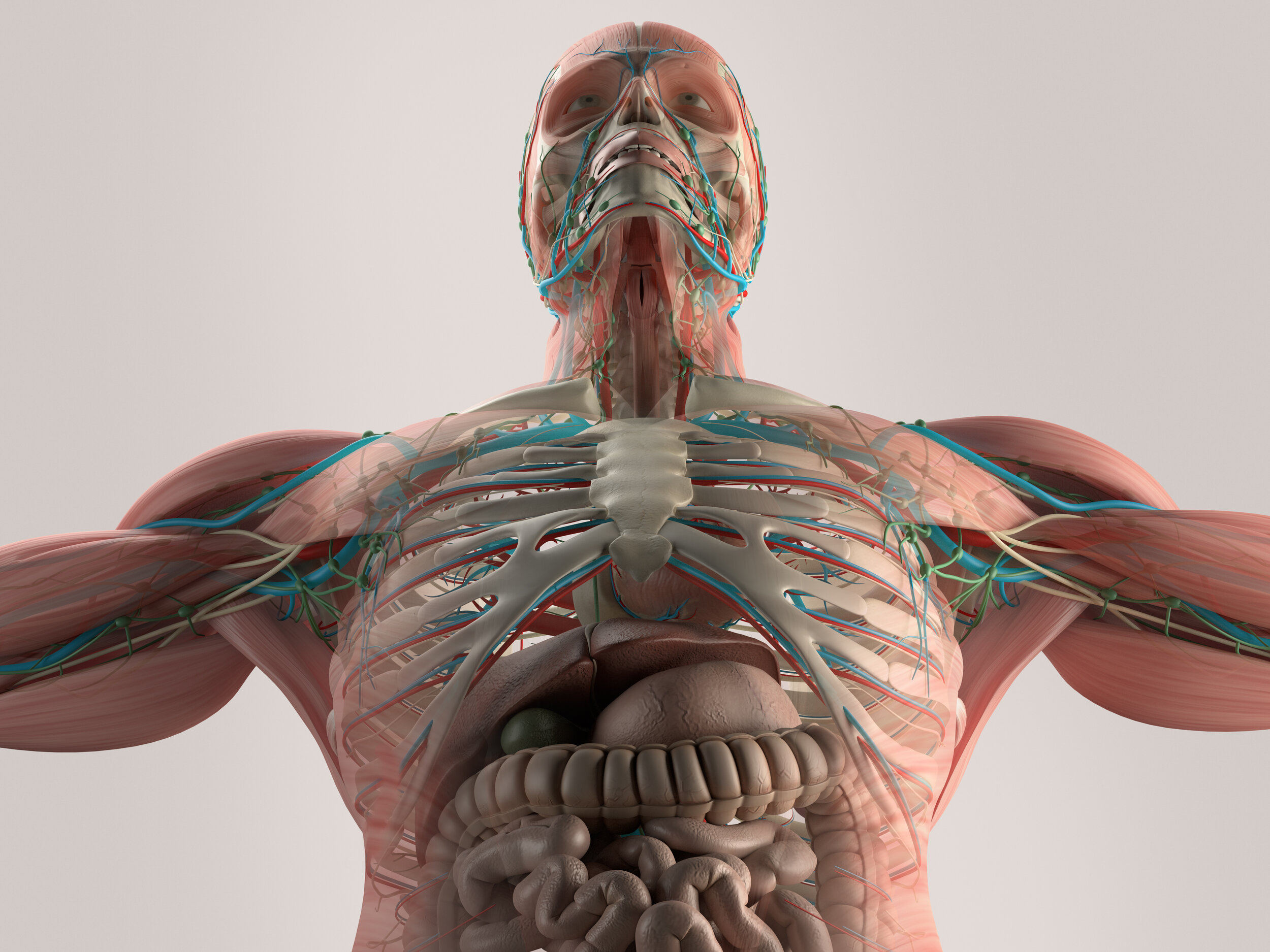
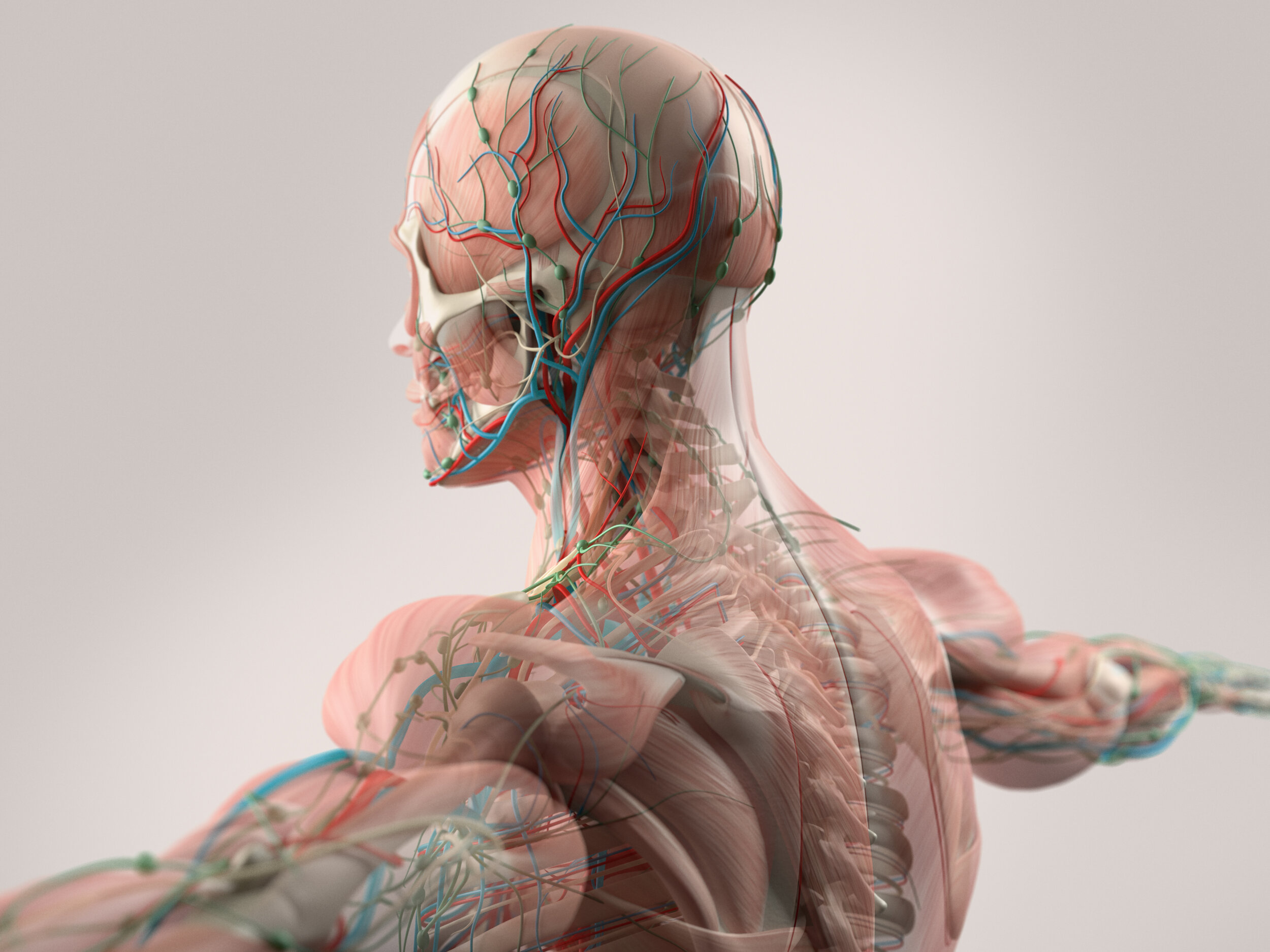
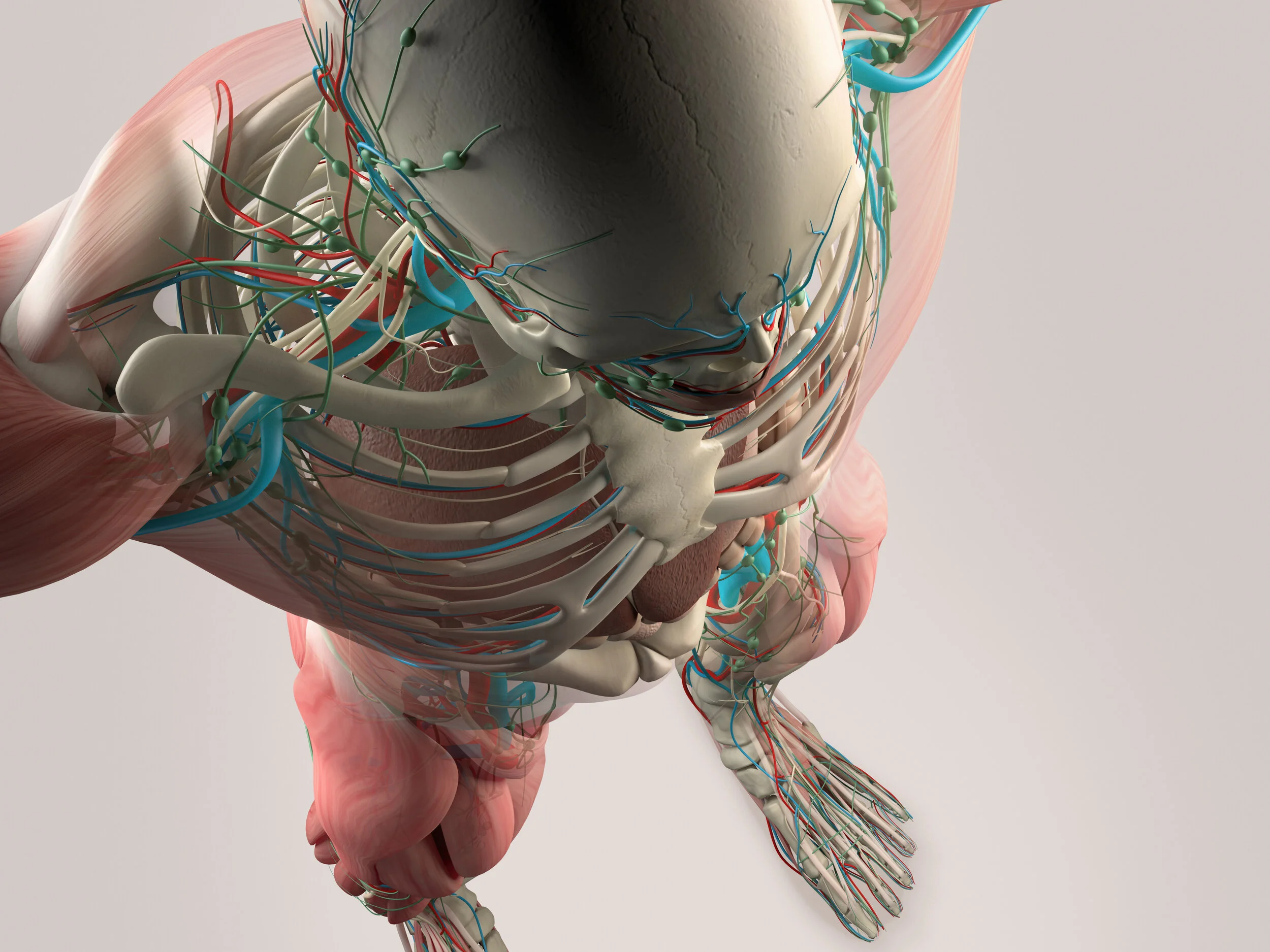
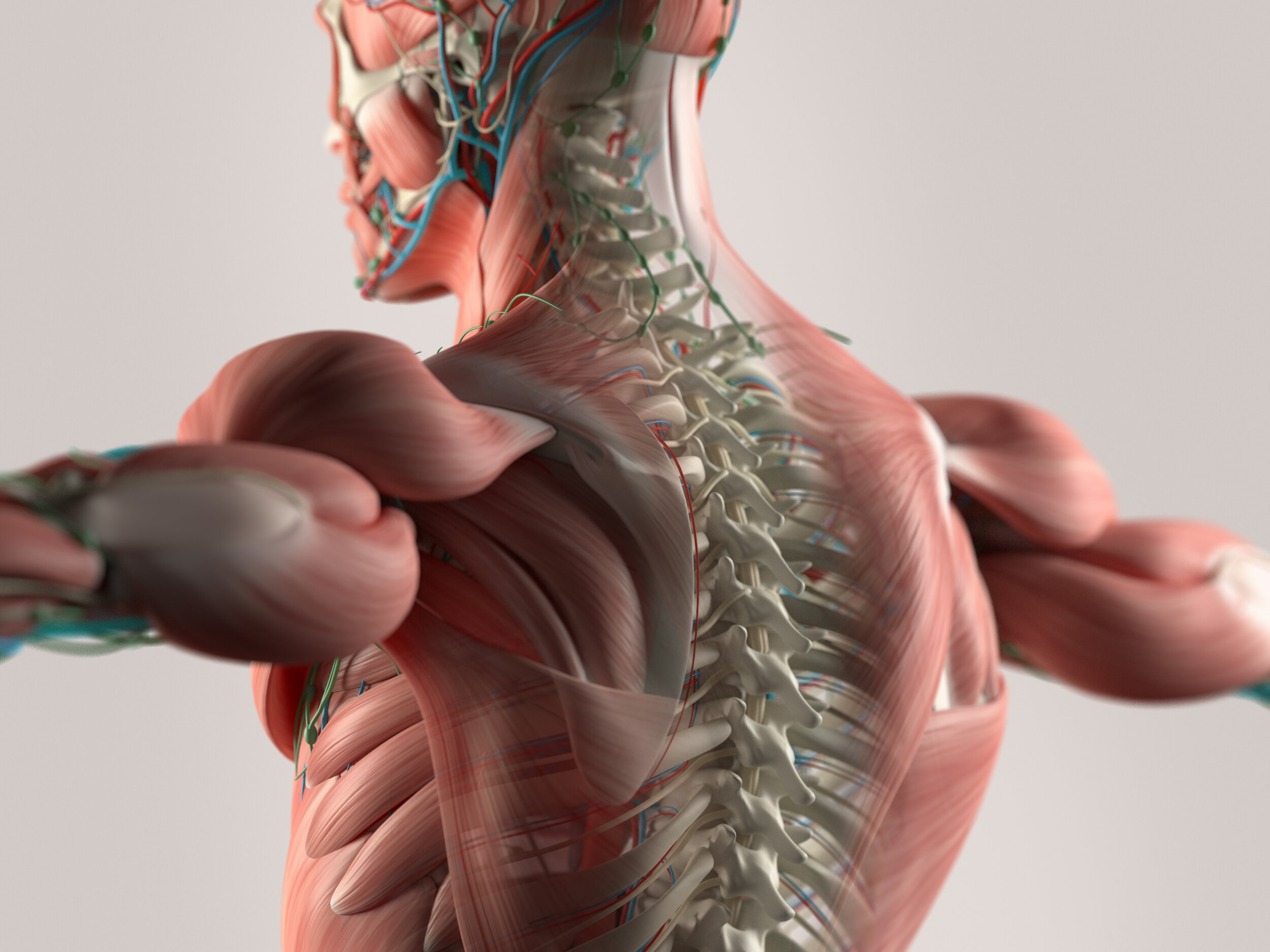
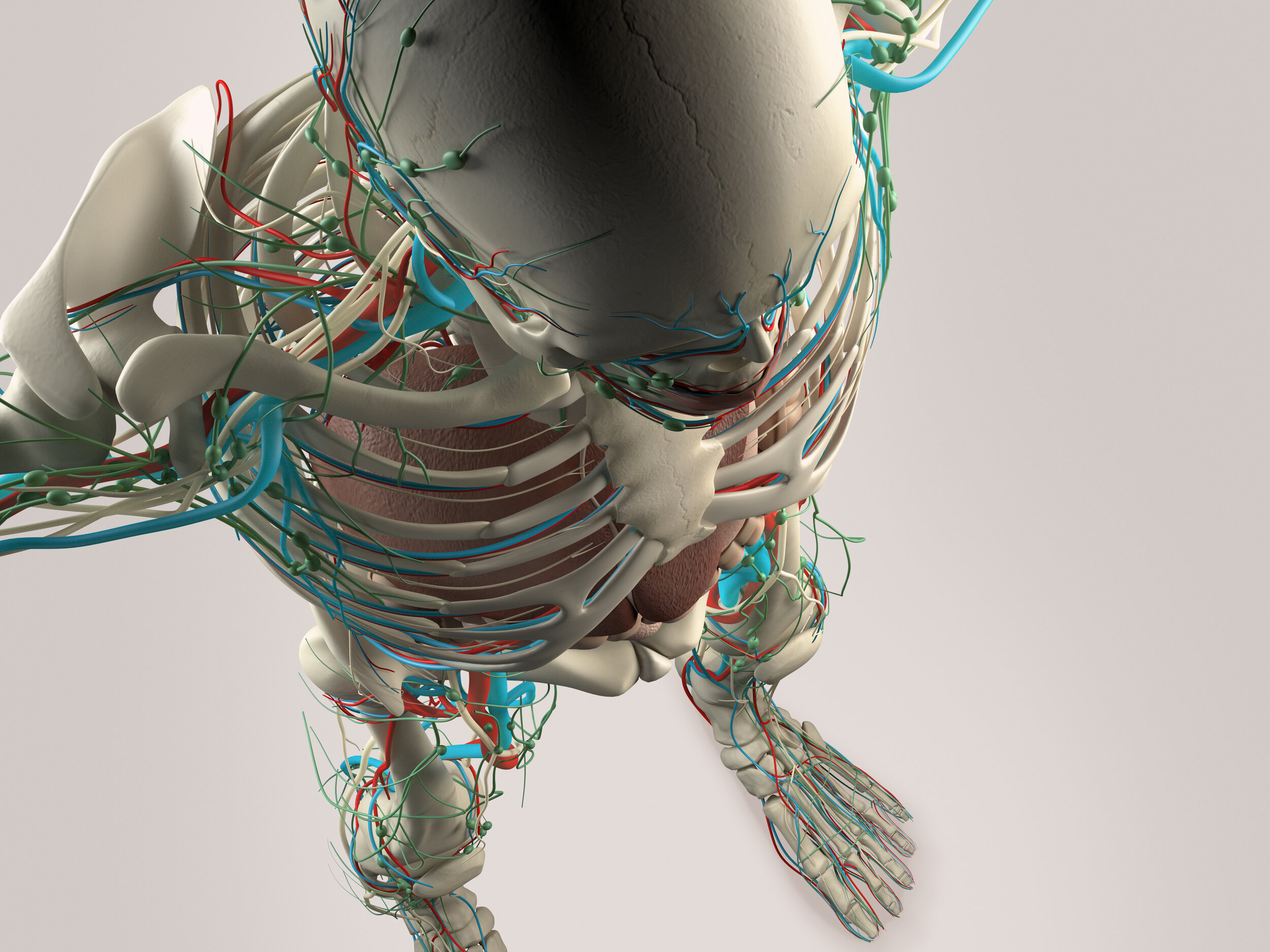
The Dynamic Human Model is an interactive and detailed anatomical model for mastering the structure of the human anatomy.
“For doctors, the human body is the focus of investigation and intervention on a daily basis; for this reason, the study of anatomy in some form will continue to be essential to safe medical practice. It is necessary for knowledge of anatomy to be assimilated by all healthcare providers in order to practice and communicate safely. Integration of newer teaching modalities and modern technology will encourage interest and retention of anatomical knowledge and its clinical relevance.”
Medical. Science. Health. Education.
Models of the human body are used by medical, science, health, and educational organizations to train medical personnel about the human anatomy, how the various parts of the body are interconnected, and how to properly treat patients. These models are also used by the same organizations to discuss medical conditions with patients so as to obtain informed consent from the patients.
The Dynamic Human Model simulates the actual physiological movement and function of the human body.
The dynamic human model includes a skeleton model in which muscles, bones, and joints provide the principle mechanics for movement, all coordinated by the nervous system. A flexible outer skin is securable over the skeleton model and the muscles, whereby a portion of the flexible outer skin may be removed for exposing the skeleton model and the muscles. When manipulated the human body's dermatome map and cutaneous innervations are shown. The dynamic human model contains nerves, arteries, and removable simulated internal organs.
SKELETAL SYSTEM
A skeleton model having a plurality of bone elements coupled together by articulating joints.
MUSCULoskeletal SYSTEM
Flexible muscles attachable to the bone elements show point of origin and insertion for contracting and stretching.
“Anatomy has a promising future. Detailed knowledge should be integrated into specialist training when it is clinically relevant allowing specialists to practice safely and accurately and also to provide a strong base for future clinical developments. ”
Subscribe
Sing up to our exclusive email list and be the first to hear of DynAtomy Labs news.
We respect your privacy.